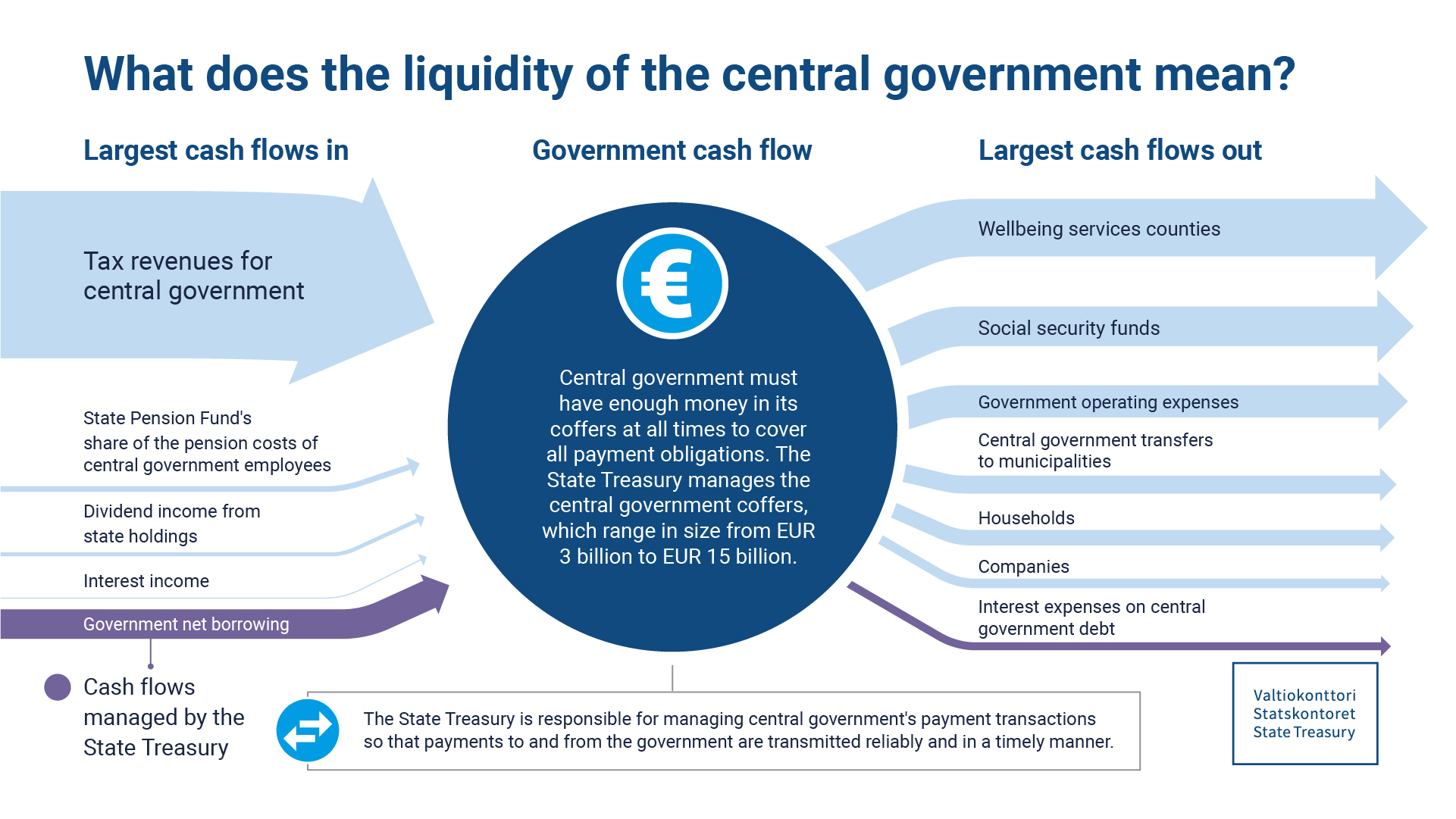
The State Treasury is responsible for the central government’s cash management. The most important function of cash management is to manage and safeguard the government’s liquidity. The size of the cash buffer is based on an assessment of sufficient liquidity and a limit on uncovered net cash flows.
Efficient cash management provides an effective overview of revenues and expenditures. The central government has a cash flow forecasting system that all central government units must use to forecast their revenues and expenditures. The central government’s cash management typically involves sizable cash flows on a daily basis. These are related to, for example, debt maturities, payment dates of central government transfers to municipalities and wellbeing services counties, and tax revenue dates. In 2023, the central government’s cash register averaged EUR 5.3 billion per month. Its cash flows are subject to monthly and annual seasonal fluctuations due to timing differences in the central government’s revenues and expenditures.
Central government’s cash funds are deposited and invested on a daily basis. The cash reserves are invested in very short-term maturities using primarily bank and central bank deposits and triparty repos. The latter means depositing funds with eligible counterparties while receiving a bond or bill as a collateral for the term of the deposit. The collateral is managed by a third party, e.g., central securities depository.